ENGR 2255 - Lab #5
Title:
- Linear Electric Circuits
Objectives:
- Gain experience with linearity and superposition
Preparation:
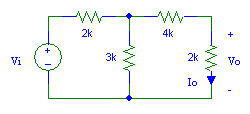
- Determine the proportionality constant K that relates Vo to Vi: Vo = K Vi in the circuit above.
- Determine the proportionality constant K that relates Io to Vi: Io = K Vi in the circuit above.
- Determine the proportionality constants K1 and K2 that relate Vo to V1 and V2: Vo = K1 V1 + K2 V2 for the circuit below.

Equipment and Parts:
- Power Supply
- Digital Multimeter(s)
- Resistors: 2 kΩ (4), 3 kΩ (2), & 12 kΩ
Procedure:
- Create the top circuit from the preparation on a proto board. Record actual values.
- Measure Vo and Io for Vi = 3V, 6V, 9V, & 12V.
- Calculate the proportionality constant that relates Vo to Vi for each set of values and determine the average.
- Calculate the proportionality constant that relates Io to Vi for each set of values and determine the average.
- Create the bottom circuit from the preparation on a proto board. Record actual values.
- Measure Vo for V1 = 9V and V2 = 12 V.
- Measure Vo for V1 = 9V and replace V2 with a short circuit. Measure Vo for V2 = 12V and replace V1 with a short circuit. Add the two measured values for Vo together. Compare the result with the value measure in the previous step.
Conclusions:
- Compare the predicted values from the preparation with the measured values from the procedure. Indicate how closely the measurements matched the predictions.
- Discuss how well linearity and superposition held.
- Discuss how well the objective was met.