ENGR 2255 - Lab #12
Title:
RLC Circuits continued
Objective:
RLC Circuits continued
Preparation:
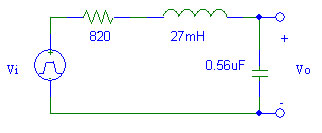
- Write the differential equation for the circuit above and obtain the characteristic equation. Solve the characteristic equation and determine the type of damping.
- Solve the differential equation for Vo assuming that Vi(t) = 5u(t). Determine the time constant.
- Use MatLab to plot the solution for Vo. (Don't do this.)
- Determine the resistor value required for critical damping.
- Repeat steps 2 and 3 for this critically damped circuit.
- Use PSpice to perform a transient analysis of this critically damped circuit. Use Probe to plot Vo. Represent Vi with a constant 5 V source and a switch that closes at t = 0. You will need to set the initial condition of the inductor and the capacitor.
- Replace the resistor with a resistor half the value of the critically damped circuit to produce an underdamped circuit.
- Repeat steps 2, 3, and 6 for this underdamped circuit.
Equipment and Parts:
- Signal Generator
- Oscilloscope
- Resistor: ~820 Ω
- Capacitor: 0.56 μF
- Inductor: 27 mH
Procedure:
- Measure the internal resistance of the inductor. Choose a resistor so that the total series resistance in the circuit produces the critically damped circuit.
- Create the critically damped RLC circuit from the preparation on a proto board.
- Use square wave generator for Vi. Set the amplitude for a 5 V step. Set the frequency so that half the period is greater than five time constants. Record the frequency.
- Observe Vo using the oscilloscope. Draw the waveform in your book.
- Create the underdamped RLC circuit from the preparation on the proto board. Again, use a resistor so that the total series resistance in the circuit is correct.
- Use a square wave generator for Vi with a amplitude of 5 V. Set the frequency appropriately.
- Observe Vo using the oscilloscope.
Conclusions:
- Compare the theoretical, predicted (simulated), and measure waveforms and time constants. If there are significant differences, suggest reasons why.
- Discuss how well the objectives were met.